Introduction to Manufacturing Technology 2 Manufacturing technology has changed immensely over the years, enabling more efficient, faster, and sa
Introduction to Manufacturing Technology 2
Manufacturing technology has changed immensely over the years, enabling more efficient, faster, and safer methods of production. Manufacturing Technology 2 is the last stage of this progression which involves complex tools and techniques employed by industries in producing high-quality goods with high accuracy. This short introduction was written out for kids like you and will make you understand the cool machines and smart technology used in making things around us.
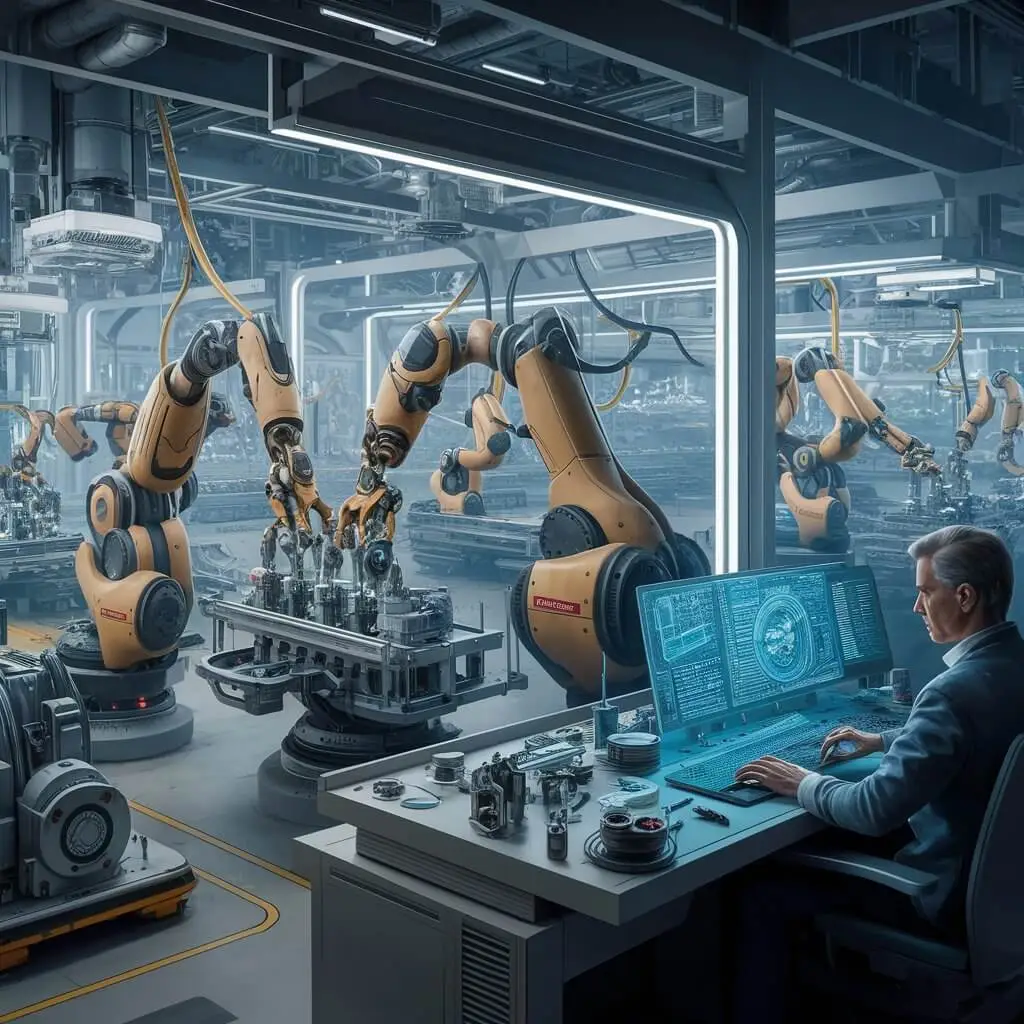
The History of Manufacturing Technologies
In earlier days, humans mostly made everything by hand. But as time went by people invented machines for making things more quickly and better. It all started from simple machines to computers and robots. And these improvements have helped create anything from toys to cars without much difficulty or danger!
Key Concepts and Definitions in Manufacturing Technology 2
To understand Manufacturing Technology 2, there are a few words we must know:
- Automation: Machines taking over jobs that humans did before.
- Precision: The ability to get it right every time.
- Innovation: Creating new ideas or processes on how we can make things better.
Core Components of Manufacturing Technology 2
Let’s look into some amazing pieces of equipment/machines that run modern manufacturing today!
Machine Tools / Equipment
These are the big machines we use to cut, shape, and join materials together to produce finished products. They come in many forms each for different types of work needed daily.
Machines categorization
- Lathes turn materials around so they can be cut into specific shapes.
- Milling Machines enable us to remove material using rotating tools and shape parts out of it.
Advancements in Equipment Technologies
Nowadays smarter technologies have emerged making them fast, and able to generate even more complicated shapes using metals such as plastics as raw materials.
Automation in Production Processes
Automation employs technology in simplifying production activities thereby reducing errors during the manufacturing process thus improving output rates.
Robotics & Programmable Logic Controllers (PLC)
Factory robots are hands that quickly and flawlessly assemble parts. On the other hand, a PLC is the brain behind the process ensuring everything runs as expected.
The Role of Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence AI lets robots and machines learn from what they do so they can improve their performance next time. It’s like having an assistant who’s smart and never forgets anything.
Material Science in Manufacturing
In making things, different materials serve different purposes. It’s like cooking where you have to choose the right ingredient for what you want to make! Here are some of the cool materials used in manufacturing.
Metals and Alloys
Metals are strong materials used to build everything from bicycles to skyscrapers. Alloys however are special blends of metals mixed to produce more strength and usefulness. For instance, stainless steel is an alloy made up of iron with some other metals which does not rust easily when used for making spoons or forks.
Polymers and Composites
Polymers are organic substances that consist of long chains of molecules. Polymers are materials that consist of high molecular masses and have a polymeric structure. Some examples include plastics (polyethylene, polypropylene), rubbers (natural rubber, butadiene rubber, nitrile rubber), and fibers (nylon, polyester). One of the most well-known polymers is plastic, which is used in everything from toys to furniture. The reason for this is that after shaping or forming a polymer in the process of manufacture it can not be returned to its initial form.
Composites are made by combining two or more materials that work better together. To make a composite material you need a matrix material that provides strength while another one fills up the gaps between them giving rigidity to the final product. A famous example is fiberglass, which combines glass and plastic to make something tough but light—perfect for boats and surfboards!
Advances in Material Processing
Technology keeps getting better at turning raw materials into amazing products. Here’s how:
Additive Manufacturing
Additive manufacturing is another term for 3D printing. Additive processes create objects by adding thin layers upon layers until they reach their desired shape. It involves building three-dimensional objects from computer-aided design models by successively adding material layer upon layer until the object is complete.
Subtractive and Deformation Processes
These are traditional ways to shape materials by cutting away what we don’t need, like carving a sculpture. In subtractive manufacturing processes, materials are removed to obtain the desired shape of an object such as carving out of wood or stone while deformative manufacturing techniques involve changing the actual shape of an object.
Manufacturing Processes and Techniques
Casting and Molding Techniques
Casting and molding are like magic tricks that turn liquids into solid objects in the shape we want using molds.
Overview of Casting Methods
Casting is the process of pouring a molten material such as metal or plastic into a mold after which it cools down and solidifies in the required shape. It’s used for making things like metal tools, car parts, and beautiful sculptures!
Innovations in Molding
Molding has gotten more advanced with technologies that allow for even more detailed and precise products. Innovations like injection molding let us make strong, lightweight items quickly and consistently, which is great for making lots of things at once.
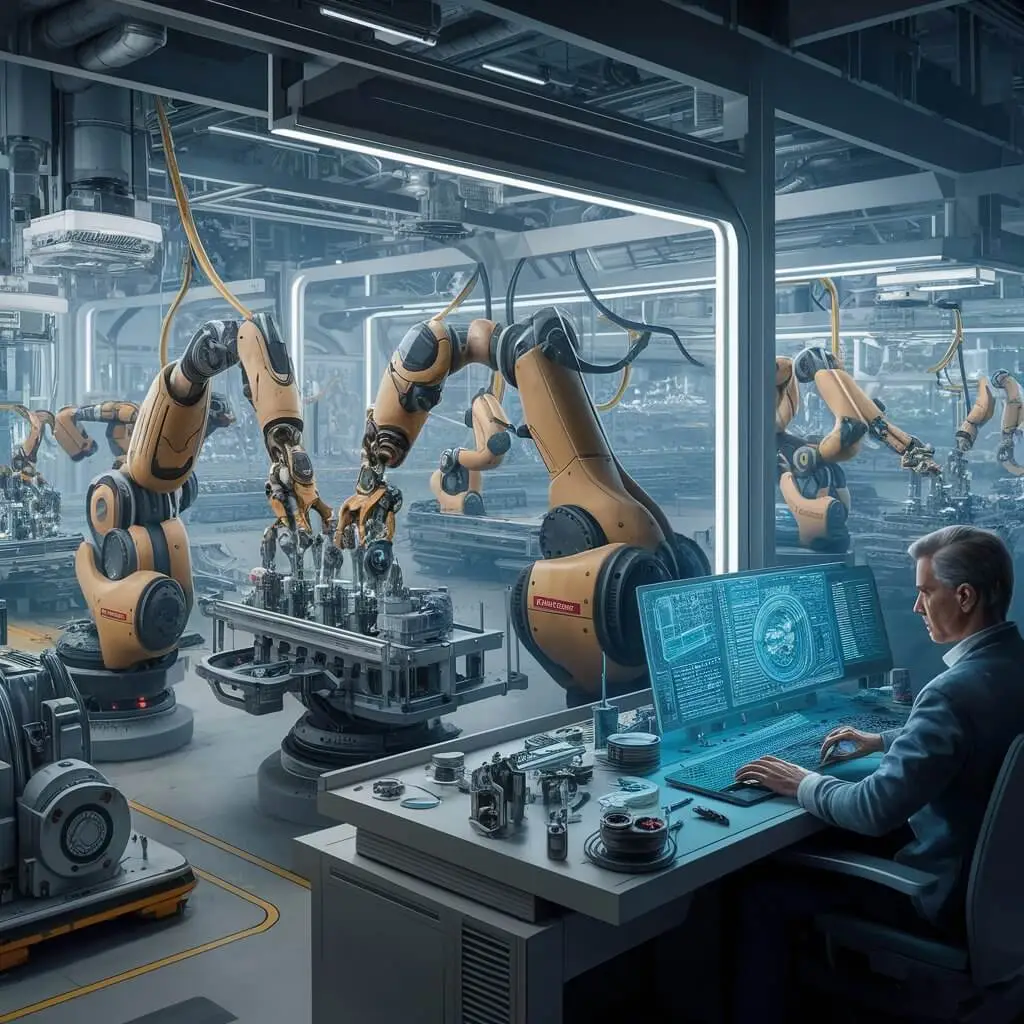
Machining and Finishing Processes
After we have the basic shape of what we’re making, we need to fine-tune it with machining and finishing touches.
Traditional vs. Advanced Machining
Traditional machining uses tools like drills and saws to cut materials into desired shapes. Conversely, advanced manufacturing encompasses laser cutting which involves using high-power laser beams focused onto the surface of an object to melt or vaporize it away.
Surface and Heat Treatment Techniques
Once a piece is shaped, surface treatment including painting can be done by polishing. After heat treatment processes are finished on an object one might find that it has no scale or decarburization on its surface. The piece can be polished to make it shiny or heated and cooled to make it stronger (a process referred to as annealing). This is very similar to baking a clay pot in a kiln so harden it up thereby ensuring that lasts longer while at the same time looking good for many years.
Quality Control and Manufacturing Management
Standards of Assurance
Producing goods in the manufacturing industry should be perfect. This is called quality assurance, which is like a detective’s search for clues to ensure everything is just right.
Methods of Measurement and Testing
If you baked cookies without tasting them to see if they needed more sugar, imagine what would happen! We measure and test products using awesome tools in manufacturing to ensure that everything is as it should be, resembling checking whether the wheels on a toy car move normally.
Standards and Certification
Following a recipe guarantees great cookies; therefore manufacturers comply with certain regulations (standards) designed to make their products safe or sturdy. Obtaining a certificate serves as a medal worn by school children that shows the product has passed all the tests.
Supply Chain Management and Operations Management
Making things does not only include constructing them but also bringing together all the components at the required place within acceptable durations.
Manufacturing Logistics
Logistics are like planning for an enjoyable road journey aimed at avoiding detours that may occur when sending materials from one place to another during production.
Inventory Control and Production Planning
Checking all our supplies before we start any big project can be likened to tallying up your school supplies. It ensures we don’t run out of anything or have too much of something else.
The Future of Manufacturing Technology
Sustainability & Green Manufacturing
Currently, there has been much talk about making things in such a way that doesn’t have harsh effects on this planet. Green manufacturing means that we can make cool stuff like this without hurting the earth.
Impact of the Internet of Things (IoT)
For example, The Internet of Things simply means how smart toys talk between themselves. In manufacturing, this implies machines can communicate thus leading to smarter production processes thereby increasing efficiency further.
Challenges and opportunities ahead
Technology is always growing, and so are the challenges and opportunities to improve things.
Addressing the Skills Gap
Many new technologies are coming up hence there is a need for skilled personnel. It involves teaching other people the same skills just like creating more superheroes with exceptional powers!
Adapting to Global Market Changes
The world keeps changing as well as how we produce things. It’s therefore comparable to learning how to play a new game but still enjoy it.
Conclusion
Manufacturing technology changes all the time, which makes it very interesting. It helps us make all the cool stuff we use every day, from toys to cars, and it’s always looking for ways to do things better and take care of our planet. Isn’t it fantastic? There are so many more ways that we can make things better and smarter!
COMMENTS